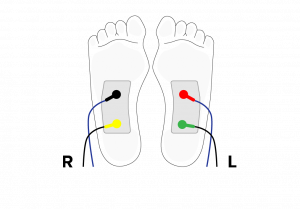
The SweatC Model A001 is a galvanic skin response technology related to the sweat gland function. It uses the sympathetic skin response (SSR) method to assess the sudomotor function via foot skin disposable electrodes following a predetermined electrical stimulations and specific sequence of measurement.
The SweatC measures the absorption of the induced sweat on the bulk of the cloth electrodes. As perspiration increases, more sweat glands are stimulated which increases the voltage amplitude in a given area of skin covered by the disposable cloth electrodes.
The test is performed in the supine position on an exam table and the patient needs to be relaxed at least 5 minutes.
Per the last published clinical study performed at the University of Miami:
The SweatC marker NO Sweat Peak had a sensitivity of 88% and a specificity of 68% (Area Under the Curve = 0.81,p< 0.0001) to detect retinopathy.
The NO Sweat Peak response marker inversely correlated with BUN (ρ=−0.41, p< 0.0001), homocysteine(ρ=−0.44,p< 0.0001), fibrinogen (ρ=−0.41, p< 0.0001), the Cardiac Autonomic Neuropathy score (ρ=−0.68, p<0.0001), and the heart rate variability Total Power (ρ=−0.57,p< 0.0001), and is positively correlated with the Photoplethysmography Index (PTGi; ρ=0.53, p< 0.0001).
The SweatC marker (Sweat Peak) inversely correlated with the severity of symptoms on the peripheral neuropathy scale (ρ=−0.56, p< 0.0001).